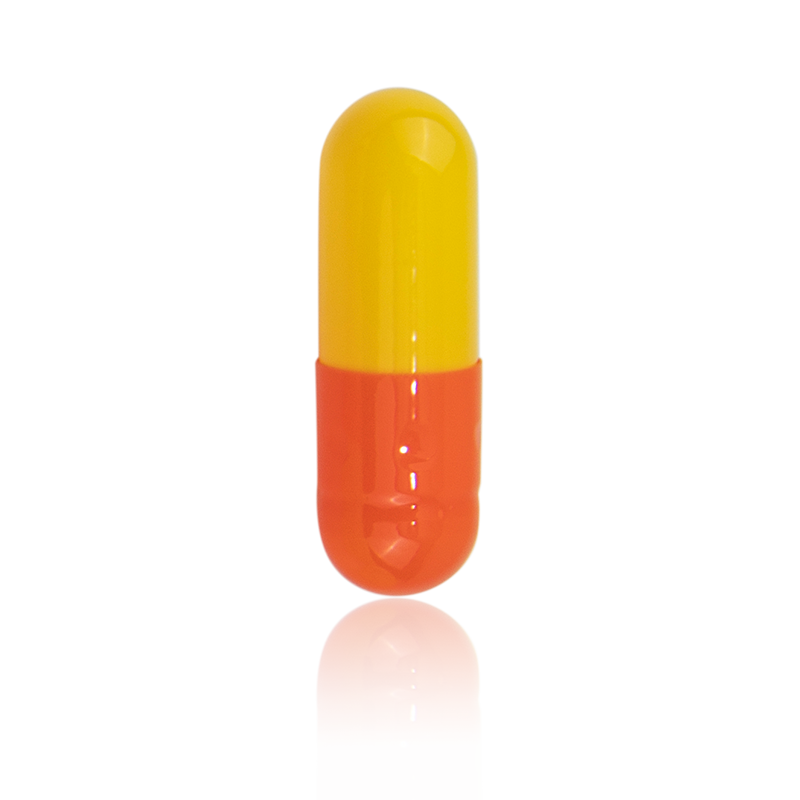
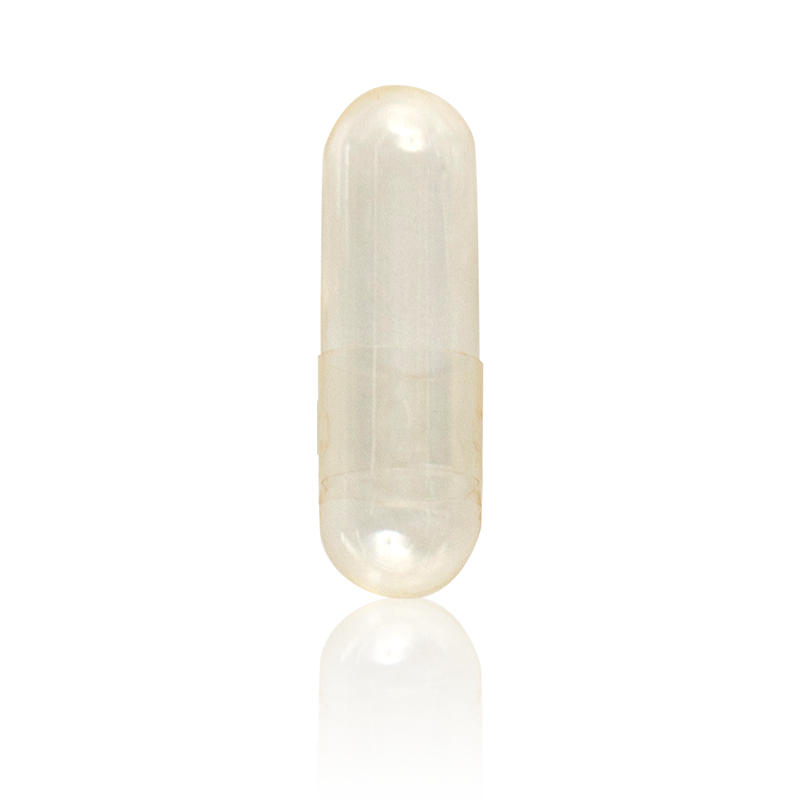
The main components of an
empty gelatin capsule are the shell and the cap. The two pieces fit together to form a container that can be filled with various substances.
The shell is the larger of the two components and is typically made of gelatin derived from animal skin or bones, although vegetarian alternatives made from plant-based materials are also available. The shell is typically clear or opaque and may be colorless or colored. Gelatin capsules are available in a range of sizes, from small sizes for powdered supplements to larger sizes for liquids or other dosage forms.
The cap is the smaller of the two components and also made of gelatin or plant-based materials. The cap fits snugly on top of the shell to complete the capsule and ensure it is leak-proof.
Both the shell and cap can be customized with different colors, flavors, and printing to make the capsule more visually appealing or to provide information such as ingredients or dosages.
Overall, empty gelatin capsules provide a convenient and versatile way to supplement or medicate, and their components should be carefully crafted to meet the needs of manufacturers and consumers.
Enteric-coated Hollow Capsules
Product introduction: Enteric gelatin hollow capsules are made of gelatin and enteric coating materials.
Product Category: Pharmaceutical Excipients
Product application: It is often used in special packaging for drugs or health care products that are irritating to the stomach or are unstable in the presence of acid, and that need to be dissolved in the intestine and exert their curative effect.
Product function: Intestinal positioning administration, reducing adverse reactions. Targeted fixed-point release: no disintegration and no cracks in gastric juice for two hours, and drug release in intestinal juice within 30 minutes, providing a perfect solution for protein polypeptide drugs and live bacteria preparations.
Product advantages: Intestinal-targeted drug delivery can improve drug efficacy and reduce dosage, and at the same time, it can reduce adverse reactions and facilitate the use of patients; it can also avoid the degradation of oral protein polypeptide drugs or health care products, providing the best absorption site for drugs.


 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体









